CaO (s) + H 2 O (l) = Ca(OH) 2 (aq) (ÎH r = 63.7 kJ/mol CaO) As the solid hydrates, an exothermic reaction occurs, causing it to puff out. Reconversion of the hydrate to quicklime is accomplished by removing the water and heating it to redness to reverse the hydration process. Calcium hydroxide is formed when one litre of water reacts with roughly 3.1 kilograms (6.8 lb) of quicklime to produce calcium hydroxide and 3.54 MJ of energy. This procedure may be used to provide a handy portable source of heat, such as for warming food on-the-spot in a self-heating container, cooking, and heating water without the need of open flames. Numerous firms provide cooking kits that use this form of heating. [11] According to the FAO, it is classified as a food additive since it acts as an acidity regulator, a flour treatment agent, and a leavener. [12] It has the E529 designation.
Multiply both the volume and density. By multiplying your two values, you may get the mass of your item. Maintain an eye on the units as you go, and you'll see that you finish up having mass units (kilograms or grams). Consider a diamond with a volume of 5,000 cm3 and a density of 3.52 g/cm3.
4 Cupric oxide's chemical formula Thus, cupric oxide's chemical formula is CuO. Quick lime is a white amorphous solid with a high melting point of 2600 degrees Fahrenheit. NH 4 2 SO 4 NH 4 2 SO 4 Because Oxygen has a valency of 2, a single Oxygen atom may meet the requirement. The ionic lattice of calcium oxide is cubic, identical to that of sodium chloride, with one ion surrounded by six opposing charge-ion. Now, divide both indices by two to get ceCaO.
Calcium oxide has the chemical formula CaO and a molar mass of 56.0774 g mol-1. The molecule is produced by an ionic connection between the calcium cation Ca+2 and the oxygen anion O-2. The ionic lattice of calcium oxide is cubic and comparable to that of sodium chloride, with one ion surrounded by six opposing charge-ion. The chemical structure of this molecule may be expressed as follows, using the standard representations for organic compounds. Calcium oxide occurs naturally as a component of the mineral Lime, which is made of calcium, magnesium, and aluminum carbonates, oxides, and hydroxides.
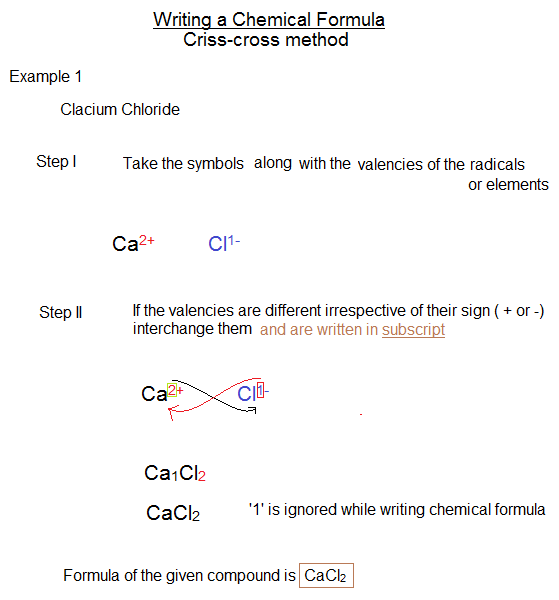
Calcium Hydroxide Formula By Criss Cross Method
It may be made in the laboratory by combining aqueous calcium chloride and sodium hydroxide solutions. Although portlandite is a very uncommon mineral, it is found in various volcanic, plutonic, and metamorphic rocks. Additionally, it has been reported to occur in burning coal heaps. In the atmospheres of S-type stars, the positively charged ionized species CaOH+ has been identified. [10]
The solubility of calcium hydroxide bases has been determined to be substantial in a variety of solvents throughout a range of immersion times. Although the optimal solubility of calcium hydroxide is unknown, some solubility is required to accomplish its therapeutic effects. Clearly, acid etching and varnishing processes must be used with caution in the presence of calcium hydroxide liners. Commercial goods have a pH of between 9.2 and 11.7. Exceeding the amount required to create calcium disalicylate induces secondary dentin in close proximity to the pulp and exhibits antibacterial action. Calcium hydroxide liners are mostly utilized in direct pulp capping and in certain regions of cavity preparation, but not for general pulpal flow lining. Due to its low fluoride release, lower solubility, and enhanced mechanical qualities, RMGI liners are a preferable option for general cavity lining.
The following table contains the names and formulae of many commonly occurring transition metal ions:
Ions of Transition Metals That Are Frequently Found 1+ 2+ 3+ 4+ copper(I), Cu + cadmium, Cd 2+ chromium(III), Cr 3+ lead(IV), Pb 4+ gold(I), Au + chromium(II), Cr 2+ cobalt(III), Co 3+ tin(IV), Sn 4+ mercury(I), Hg 2+ cobalt(II), Co 2+ gold(III), Au 3+ silver, Ag + copper(II), Cu 2
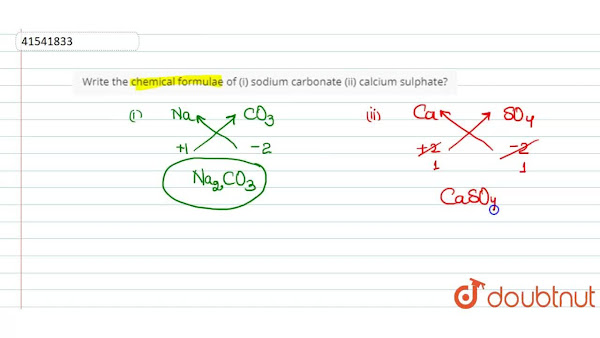
Formulas for Determination This is referred to as the Criss-Cross Method. Examples Na+1 + O-2 Ca+2 + P-3 C+4 + O-2 Sodium dioxide C 2 O 4 is converted to CO 2. Compound Naming. Chemical Nomenclature --> A nomenclature system is a method for naming chemical compounds. Calculating rate constants using the relaxation approach -. After a perturbation, the system (a â b) may acquire a new rate constant.
Chemical Formula Of Calcium Oxide By Criss Cross Method
When two non-metals are covalently bound, the name may be expressed using prefixes. Typically, the number of atoms in each constituent in a molecule is denoted by the prefix: single atom - hexa atomic nuclei diatomic atoms - hepta-atomic nuclei tri-atomic particles - octa atomic nuclei tetraatomic nuclei penta atoms penta atoms penta atoms 11 Nomenclature of Molecules Examples: NO2 is nitrogen dioxide.
David Hume tells in his History of England that during Henry III's reign, the English Navy annihilated an invading French fleet by blinding it with quicklime.
[24] Quicklime may have been utilized in medieval maritime warfare – up to the point of being thrown at enemy ships by "lime-mortars." [25] [edit] Substitutes
Chemical substances in industrial glass Limestone (calcium carbonate) or dolomite (calcium magnesium carbonate) are used to make lime when magnesium oxide is also required. It was typical in the past to add around 0.25 percent arsenic oxide and 0.5 percent sodium nitrate to help in glass fining, or the removal ofâ Continue reading
It is a solvent. Penthrane and neothyl fluothane Chloroform is still utilized in a number of applications today. It is used. CDCl 3 is a solvent that is often used in NMR spectroscopy. Deuterochloroform is formed when acetone or ethanol reacts with sodium hypochlorite or calcium hypochlorite in a haloform reaction. Humans use organic molecules in a variety of ways.
Molecular Formula Of Calcium Oxide By Criss Cross Method
A compound containing a transition metal must be named in such a way that the metal's oxidation state is specified. Following the metal is a Roman number. It denotes the metal's oxidation state. Ex. Iron (FeCl3) (III) Chloride Copper chloride (II) Assigning Oxidation # Transition Metals Chloride6
Calcium oxide has a broad variety of applications and is frequently utilized today. The compound is necessary for building work since it is a component of high-quality steel, cement, mortar, and plaster. Additionally, it is used in the making of rubber, soap, varnish, and refractories, as well as in the creation of pharmaceutical items, insecticides, and plant and animal feeds. It is used in agriculture to improve the soil's quality. As previously noted, it is a component of some silicate glass products and is used to manufacture calcium carbide, basic calcium nitrate, and calcium bisulphite. Additionally, it is used to de-hair animal skins. [1] [4] Lime has been used in one other theatrical production. Prior to the invention of electric lighting, lime was cooked to an extremely high temperature till it gave out a dazzling incandescent glow. These were utilized as stage lights, which is how the phrase "lime light" originated. [1]
Chemical substances in industrial glass Limestone (calcium carbonate) or dolomite (calcium magnesium carbonate) are used to make lime when magnesium oxide is also required. It was typical in the past to add around 0.25 percent arsenic oxide and 0.5 percent sodium nitrate to help in glass fining, or the removal ofâ Continue reading
WRITING COMPOUNDS: â Begin by writing the metallic element's symbol. â Designate one element's combining capability as a subscript of the other element. â Eliminate all subscripts with a value of 1. • NAMING COMPOUNDS: â Begin with the whole name of the metal ion. â Rename the non-metal by omitting the final â and adding the suffix âideâ. Brackets are used to indicate the number of electrons given out by the Transition metal.